Welcome to wellhealthorganic.com, your ultimate guide to exploring vegetarian protein sources. In today’s health-conscious world, many individuals are opting for vegetarian or plant-based diets for various reasons, including ethical, environmental, and health concerns. As such, understanding and incorporating adequate protein sources into a vegetarian diet is crucial for maintaining optimal health and wellness.

Why Do We Need Proteins?
- Muscle Growth: Protein consumption enhances muscle protein synthesis, aiding in muscle growth and increasing strength and stamina.
- Metabolism Booster: Protein boosts metabolism and aids weight loss by building muscle mass, which increases fat burning.
- Immunity Boost: Regular protein intake supports the production of hemoglobin, immunoglobulins, and enzymes, boosting immunity and aiding in tissue repair and recovery.
- Aging Support: Adequate protein intake helps reduce age-related muscle loss and health issues, maintaining joint health over time.
Types and Categories of Vegetarian Protein Sources
| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Legumes | Lentils, Chickpeas, Black beans, Kidney beans |
| Nuts and Seeds | Almonds, Walnuts, Chia seeds, Hemp seeds |
| Grains | Quinoa, Brown rice, Barley, Oats |
| Soy Products | Tofu, Tempeh, Edamame, Soy milk |
| Dairy and Dairy Alternatives | Greek yogurt, Cottage cheese, Almond milk, Coconut yogurt |
| Vegetables | Spinach, Broccoli, Brussels sprouts, Peas |
| Seitan (Wheat Gluten) | Textured vegetable protein, Seitan strips |
How Much Protein Do Indians Need?
In the daily intake should be 0.8 to 1g of protein per kg body weight, meaning a person weighing 70 kg needs about 70 grams of protein daily.
Symptoms and Signs of Protein Deficiency
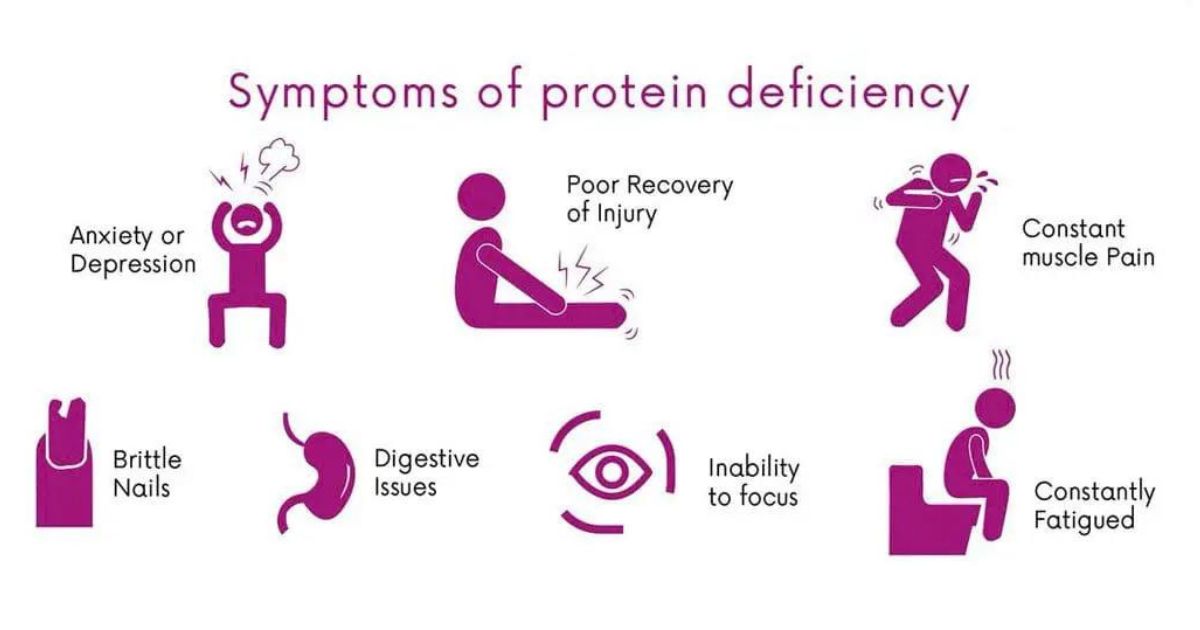
Despite the abundance of vegetarian protein sources, inadequate intake can lead to symptoms of protein deficiency, such as:
- Muscle weakness
- Fatigue
- Edema (swelling)
- Hair loss
- Slow wound healing
Causes and Risk Factors for Inadequate Protein Intake
Several factors can contribute to inadequate protein intake on a vegetarian diet, including:
- Lack of knowledge about protein-rich plant-based foods
- Limited access to diverse vegetarian options
- Dietary restrictions or preferences
- Underlying health conditions affecting nutrient absorption
Diagnosis and Tests for Protein Deficiency
Diagnosing protein deficiency typically involves a comprehensive assessment by a healthcare professional, including:
- Evaluation of dietary habits and intake
- Blood tests to measure serum protein levels
- Physical examination to assess symptoms and signs of deficiency
Treatment Options for Protein Deficiency
Addressing protein deficiency often involves:
- Dietary modifications to include more protein-rich foods
- Supplementation with plant-based protein powders or supplements
- Collaboration with a registered dietitian or nutritionist for personalized guidance
Preventive Measures for Maintaining Adequate Protein Intake
To prevent protein deficiency on a vegetarian diet, consider the following tips:
- Include a variety of protein sources in your meals and snacks
- Plan balanced vegetarian meals that combine grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and vegetables
- Be mindful of portion sizes to ensure adequate protein intake without excessive calories
Personal Stories or Case Studies
Case Study 1: Emily’s Journey to Plant-Based Protein
Emily, a lifelong vegetarian, struggled with fatigue and muscle weakness despite her otherwise healthy lifestyle. Upon consulting with a nutritionist, she discovered the importance of incorporating diverse plant-based protein sources into her diet. With guidance, Emily revamped her meals to include a variety of legumes, nuts, seeds, and soy products. Over time, she noticed significant improvements in her energy levels and overall well-being.
Case Study 2: Mark’s Transformation with Vegan Protein
Mark, a fitness enthusiast, transitioned to a vegan diet to align with his ethical beliefs. Concerned about maintaining muscle mass and strength, he sought advice from a sports nutritionist specializing in plant-based diets. By strategically incorporating vegan protein sources like tofu, tempeh, and pea protein supplements into his meal plan, Mark not only preserved his physique but also achieved new fitness milestones.
FAQS
1. Are vegetarian protein sources sufficient for meeting daily protein requirements?
Yes, vegetarian protein sources can provide all the essential amino acids necessary for meeting daily protein needs when consumed in adequate amounts and variety.
2. How can I ensure I get enough protein on a vegetarian diet?
You can ensure adequate protein intake by including a variety of protein-rich plant foods such as legumes, nuts, seeds, soy products, dairy or dairy alternatives, grains, vegetables, and seitan in your meals and snacks.
3. Are there any vegetarian protein sources that contain complete proteins?
Yes, soy products such as tofu, tempeh, and edamame are considered complete proteins, as they contain all nine essential amino acids required by the body.
4. Can I build muscle on a vegetarian diet?
Yes, it is entirely possible to build and maintain muscle mass on a vegetarian diet by consuming a balanced mix of protein-rich plant foods and engaging in regular strength training exercises.
5. Are there any risks associated with consuming too much protein from vegetarian sources?
While protein is essential for overall health, excessive intake from any source, including vegetarian sources, can potentially strain the kidneys and may lead to other health issues. It’s essential to maintain a balanced diet and avoid overconsumption of protein.
6. Can individuals with soy allergies still meet their protein needs on a vegetarian diet?
Yes, individuals with soy allergies can still obtain adequate protein from other sources such as legumes, nuts, seeds, grains, dairy or dairy alternatives, vegetables, and seitan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Wellhealthorganic.com Vegetarian Protein is key to maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet on a plant-based lifestyle. By incorporating a diverse range of legumes, nuts, seeds, grains, soy products, and vegetables, individuals can easily meet their protein requirements while reaping the numerous health benefits associated with plant-based eating.
Remember, whether you’re a seasoned vegetarian or considering a transition to a plant-based diet, wellhealthorganic.com is your go-to resource for all things related to vegetarian nutrition and wellness.
